I will give you the rundown of how this very simple code works.
x = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(hex(x))
x is our variable. It holds a value.
int tells Python that we are using integers (regular numbers).
input uses the string (text in quotes) to display the message to user to tell them to enter a number. When int is used, the only thing that can be used is a number. Python is smart this way.
print... prints the expression in the parentheses. In this case, it prints the answer to the operation (the decimal conversion).
Now, what about the parentheses? This is where a lot of beginner programmers have trouble with... it took me a few minutes too, so don't worry.
The parentheses tell Python what to do first; much like BEDMAS (or whatever it's called). Whatever is in the middle parentheses is done first, then the outer, then so on and so forth. The first line in the code asks for user to enter a number. Checks if value entered is an integer. If it is, it takes the inputted number and stores it in the variable x. Then proceeds to the next line. The second line gets the value entered into the variable x, and then converts to hex. Finally, the operation output is printed.
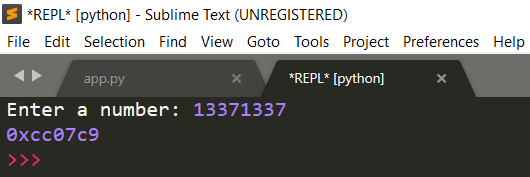
That's it! Simple, isn't it?
x = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(hex(x))
x is our variable. It holds a value.
int tells Python that we are using integers (regular numbers).
input uses the string (text in quotes) to display the message to user to tell them to enter a number. When int is used, the only thing that can be used is a number. Python is smart this way.
print... prints the expression in the parentheses. In this case, it prints the answer to the operation (the decimal conversion).
Now, what about the parentheses? This is where a lot of beginner programmers have trouble with... it took me a few minutes too, so don't worry.
The parentheses tell Python what to do first; much like BEDMAS (or whatever it's called). Whatever is in the middle parentheses is done first, then the outer, then so on and so forth. The first line in the code asks for user to enter a number. Checks if value entered is an integer. If it is, it takes the inputted number and stores it in the variable x. Then proceeds to the next line. The second line gets the value entered into the variable x, and then converts to hex. Finally, the operation output is printed.

That's it! Simple, isn't it?




 Discord: SnB_BWH
Discord: SnB_BWH



